The Comprehensive Guide To GSM Network: Understanding Its Structure And Functionality
GSM Network, also known as Global System for Mobile Communications, is a standard developed to describe protocols for second generation (2G) digital cellular networks used by mobile phones. This technology has revolutionized the way we communicate and has become the backbone of mobile communication globally. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of GSM, exploring its architecture, components, and the role it plays in modern telecommunications. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will have a thorough understanding of GSM networks and their significance in our daily lives.
The importance of GSM networks cannot be overstated; they facilitate not only voice calls but also text messaging and mobile internet access. Since its inception in the 1990s, GSM has evolved significantly, incorporating various enhancements and improvements that have increased its efficiency and capabilities. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of GSM networks, ensuring that you grasp both the fundamental concepts and advanced topics related to this crucial technology.
This guide is structured to provide a logical flow of information, beginning with the basic definitions and moving towards more complex aspects of GSM networks. Whether you are a telecommunications professional, a student, or just an interested reader, this article will serve as a valuable resource for understanding GSM technology and its implications in the modern world.
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to GSM Network
- 2. Architecture of GSM Network
- 3. Key Components of GSM Network
- 4. Functionality of GSM Network
- 5. Advantages of GSM Network
- 6. Challenges Faced by GSM Networks
- 7. The Future of GSM Technology
- 8. Conclusion
1. Introduction to GSM Network
The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is a digital mobile network that uses a variation of time division multiple access (TDMA) to allow multiple users to share the same frequency channel. Originally developed in Europe, it has become the most widely adopted mobile communication standard worldwide. GSM is recognized for its high-quality voice transmission and capacity for data services, making it a preferred choice for mobile operators.
Historically, GSM was developed to replace earlier analog systems, providing a more efficient and secure means of communication. Its introduction marked a significant turning point in mobile technology, leading to the proliferation of mobile devices and services we enjoy today. The GSM standard has been adopted in over 200 countries and serves billions of users globally.
Understanding GSM networks involves exploring their underlying architecture, key components, and operational functionality. This foundational knowledge is essential for anyone interested in telecommunications, mobile technology, or related fields.
2. Architecture of GSM Network
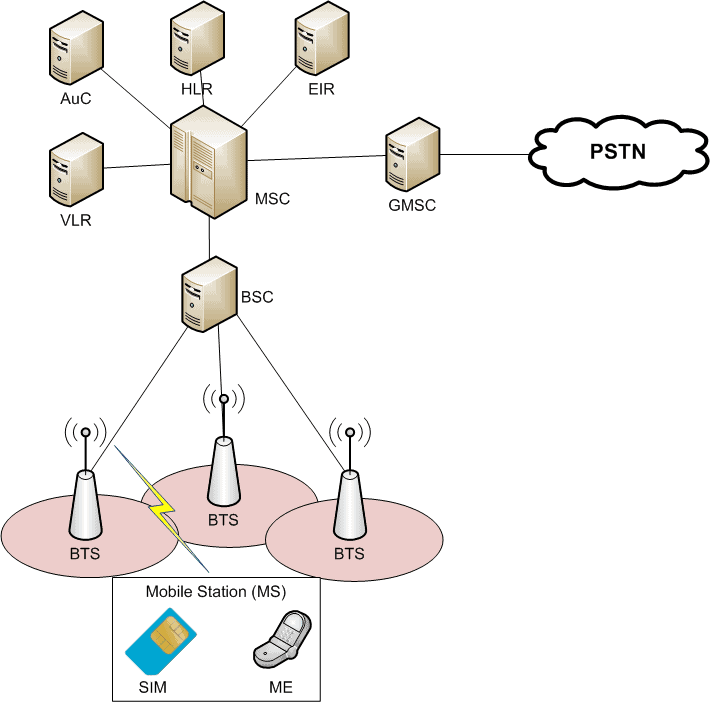
The architecture of a GSM network is designed to support mobile communication effectively. It is divided into several key subsystems, each with specific functions. The main components of the GSM architecture include:
2.1 Mobile Station (MS)
A mobile station consists of the mobile device and the SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) card. The SIM card stores user information and allows the device to connect to the network.
2.2 Base Station Subsystem (BSS)
The BSS is responsible for handling radio communication between the mobile station and the network. It consists of:
- Base Transceiver Station (BTS): Responsible for radio communication with mobile devices.
- Base Station Controller (BSC): Manages multiple BTS units and controls their radio resources.
2.3 Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS)
The NSS is the core of the GSM network, responsible for call routing and switching. It includes:
- Mobile Switching Center (MSC): The central component that connects calls and manages mobile services.
- Home Location Register (HLR): A database that stores user subscription details and service information.
- Visitor Location Register (VLR): Temporarily stores information about users currently within the MSC's area.
2.4 Operation Support Subsystem (OSS)
The OSS monitors and maintains the GSM network, ensuring quality of service and troubleshooting issues as they arise.
3. Key Components of GSM Network
Each component of the GSM network plays a vital role in ensuring seamless communication. Below are the key components and their functions:
3.1 SIM Card
The SIM card is essential for user authentication and identity verification. It contains unique information such as the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) and security keys for encrypted communication.
3.2 BTS and BSC
The BTS connects mobile devices to the network, while the BSC manages the frequency channels and handovers between BTS units to maintain call quality.
3.3 MSC and HLR
The MSC routes calls and manages mobile services, while the HLR stores data about the user, including their subscription details and current location.
3.4 GPRS and EDGE
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) and Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE) are technologies that enable data transmission over GSM networks, allowing users to access mobile internet services.
4. Functionality of GSM Network
The functionality of a GSM network revolves around its ability to provide reliable communication services. Key functionalities include:
4.1 Call Establishment
When a user initiates a call, the mobile device communicates with the nearest BTS, which forwards the request to the MSC. The MSC then routes the call to the recipient's MSC, establishing a connection.
4.2 SMS Services
GSM networks support Short Message Service (SMS), allowing users to send and receive text messages. This service relies on the Short Message Service Center (SMSC) to store and forward messages.
4.3 Mobile Data Services
With the introduction of GPRS and EDGE, GSM networks can provide mobile internet access, enabling users to browse the web, send emails, and use various applications on their devices.
5. Advantages of GSM Network
The GSM network offers several advantages that contribute to its widespread adoption:
- Global Standard: GSM is recognized worldwide, facilitating international roaming and interoperability among different mobile networks.
- Security: GSM networks employ encryption and authentication mechanisms to ensure secure communication.
- Efficient Spectrum Utilization: The TDMA technology used in GSM allows for efficient use of available frequency bands.
- Support for Multiple Services: GSM supports voice, SMS, and data services, making it versatile for various communication needs.
6. Challenges Faced by GSM Networks
Despite its advantages, GSM networks face several challenges:
- Limited Data Speeds: While GPRS and EDGE improved data capabilities, they still lag behind newer technologies like 3G and 4G.
- Capacity Issues: In densely populated areas, the demand for voice and data services can exceed the network’s capacity.
- Interference: GSM networks can experience interference from other electronic devices, impacting call quality.
7. The Future of GSM Technology
As technology continues to evolve, the future of GSM networks is increasingly focused on integration with newer mobile technologies. Future developments may include:
- Migration to 5G: Many operators are transitioning to 5G networks, which promise significantly higher data speeds and lower latency.
- IoT Integration: GSM technology is expected to play a role in the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT), connecting various devices to the network.
- Improved Security: Ongoing advancements in encryption and authentication will enhance the security of GSM communications.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, the GSM network has played a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of mobile communication. Its architecture, key components, and functionalities demonstrate its significance in providing reliable communication services worldwide. While it faces challenges, advancements in technology promise a bright future for GSM and its integration with newer systems.
We encourage readers to engage with this content by leaving comments, sharing the article, or exploring additional resources on our site to expand their understanding of telecommunications and mobile technologies.
Thank you for taking the time to read this comprehensive guide on GSM networks. We hope to see you back soon for more insightful content!
Nigerian Actress Who Died Recently: Remembering The Legacy
Marmaduke Mickey Percy Grylls: The Adventure Of A Lifetime
Kiara Mia: The Rise Of A Star In The Adult Film Industry